How to Survive a Portuguese Man o War Sting


Possibly laying claim to the best animal name ever, the Portuguese man o’ war (aka man-of-war or blue bottle) isn’t actually a single animal at all. It’s a colony of variations of the same organism that carries out specialized tasks. One colony is known as a single man o’ war. Several floating colonies together are called a legion! And you definitely don’t want to find yourself swimming through a legion of them!
Individuals within the colony can’t live independently, so you might want to think of them a bit more like a giant group of conjoined twins. Each is unique but dependent on the others to help the colony as a whole.
There are 4 major types of individuals in the colony (each type is called a zooid). One is specialized to keep it afloat, one for digestion, one for reproduction, and one for hunting. The hunting zooid are the ones we’re most concerned with. They’re the ones that make up the stinging tentacles!
These colonies can’t swim and are thus at the mercy of the currents. That means that while they may prefer the open ocean, in certain weather conditions, they can start washing up on the shore and will get close to where humans often swim.
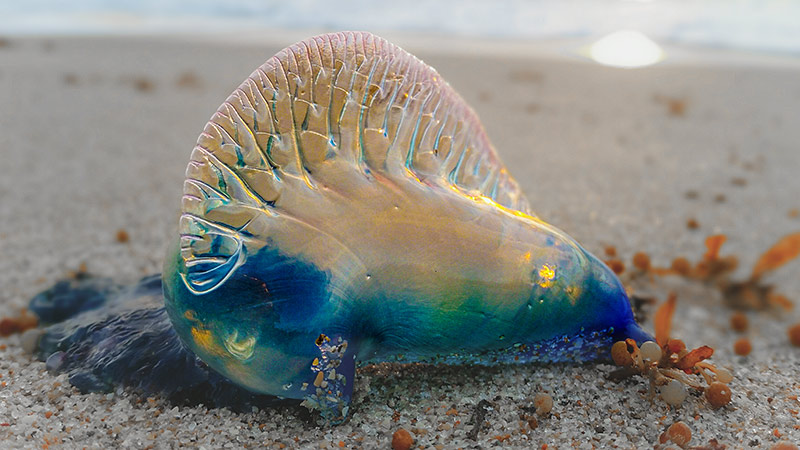

All cnidarians have tentacles with stinging cells. They’re a group that includes 11,000 species which include the corals, anemones, hydrozoans and jellyfish. The Portuguese man o’ war makes our list not because it’s the most deadly floating cnidarian (the box jelly which I deal with next takes that prize), but because it stings more people each year than any other cnidarian. In fact, tens of thousands of people are stung by them yearly. These encounters result in long, often open wounds on the skin caused by the irritating toxic substances in the tentacles. They leave intense dark purple marks, often in the exact outline of the tentacles that touch the skin. Most remain forever.
Deaths are rare, but I’ve found at least two confirmed cases – one in Florida and one in Italy. Both seemed to be the result of anaphylactic shock (an intense allergic reaction).
Even if death is rare, you do want to know how to stay away from them, and how to not make the sting of the tentacles any worse than they already are.

What causes the “stings”?
The best way to think about this is that the “hunting” type zooids that make up the tentacles contain little spherical capsules that, when triggered, can fire little darts which inject venom. These capsules are called nematocysts, and they’re incredibly cool biological venom-injecting structures unique to this animal phylum.
This system is designed to quickly capture and incapacitate swimming prey in the ocean. Because of these nematocysts, they’re exceedingly powerful hunters.
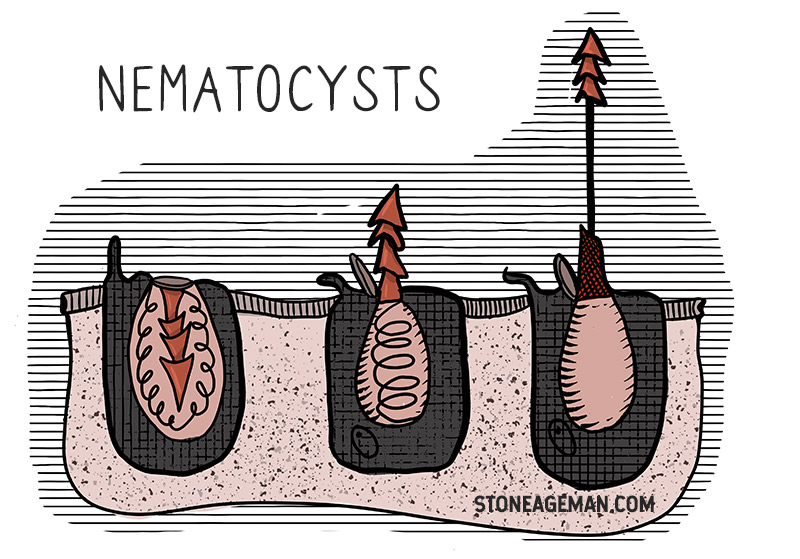
You can trigger a nematocyst to fire it’s harpoon-like venom-dart through touch, electricity, or a change in salinity.
The reason it’s important to know a bit about nematocysts and how they fire is that the treatment and prevention of stings relates to figuring out how to keep them from firing. We’ll get to sting prevention, but first let’s look at treatment if you get stung.
Treatment for a Portuguese Man o’ War Sting
The treatment is simple. Get the stinging tentacles off your body without causing more of the venom-filled nematocysts to fire. That means…
- Don’t rub them off. The physical rubbing will cause them to sting.
- Don’t rinse with freshwater or alcohol. The change in salinity will also cause unfired nematocysts to release more venom.
- Don’t pee on it: Contrary to popular belief, this is both gross and not effective. It’s pretty likely that your pee will cause the nematocysts to fire.
- Rinse with saltwater or even better, vinegar. This will keep the nematocysts from firing.
- If you need to pull tentacles off, pull them off gently and carefully, trying not to let them touch other parts of your skin.
- You may not be able to see some tentacles or barbs that are stuck in your skin. Because of this you could cover the area in shaving cream and then shave the skin. This will hopefully clean it properly.
- For pain, add heat around 115 degrees F for 45 minutes. That’ll neutralize the toxins that are in the body already. For reference, that’s not quite as hot as a standard heating pad gets. You don’t want to burn yourself.
- Hydrocortisone can also be used for pain relief.
How many people die from Portuguese Man-o-Wars?
In 2010, a woman swimming off the coast of Sardinia died from what was believed to be anaphylactic shock from an encounter with a man o’ war. Another fatal sting occurred off the Florida Atlantic coast in 1987. Both occurred when a swimmer got tangled up in the tentacles. One can only assume these incidents were on highly susceptible individuals. Then again, we can’t know for sure. Deaths are rare. There may be other accounts, but these are the few well documented cases.

Scenarios to Avoid with Jellyfish
Portugese man o’ wars often get washed up on beaches. Since they don’t actively swim, this is a good indication that weather conditions have changed and are blowing them into shallow waters. Avoid swimming without some protective covering if the beach is littered with them. And definitely don’t touch the ones that have washed up onto shore.
Most importantly, if you’re swimming and do get stung – stop, look around, and try not to get entangled more.
The Most Dangerous Man o war
Technically there are ~20 species of marine hydrozoans in the family Physaliidae that we might call man o’ wars. The number is not precisely known as most are open ocean species that are not well studied. The two that are most common are the Portugese man o’ war (Physalia physalis) and the Pacific man o’ war (Physalia utriculus). Both are pretty similar, and often called the same thing, so I’m grouping them together here under the same name.
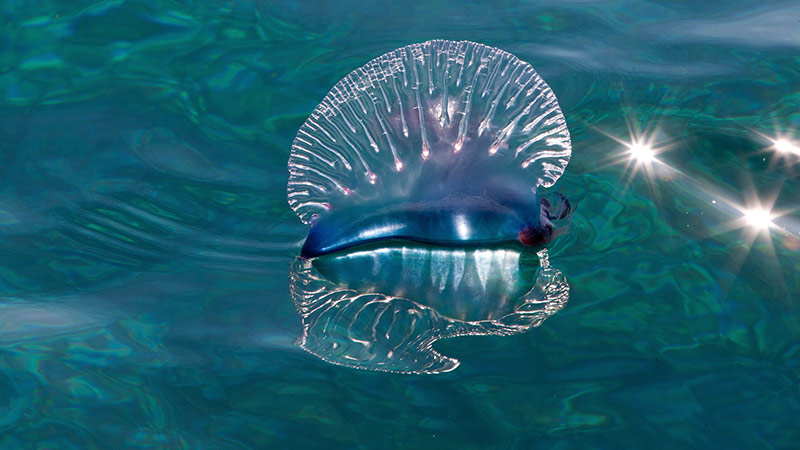

How to Survive a Portuguese Man o’ War sting
If you do happen to be swimming in the ocean and you feel something sting you, stop. Try to remain calm. You don’t want to panic as it could get worse. If it is a man-of-war, the tentacles could be up to 165’ long. Thrashing around will only wrap the tentacles around you.
Now, look around. Let’s hope you’re not in a legion (a group of man o’ wars). What you’re trying to do is get out of the water and avoid excessive stings that could cause you to go into anaphylactic shock. Follow the proper first aid outlined above and seek medical care if things don’t get better.
If you see one on the beach or floating by from a safe distance, stop for a second and admire the amazing complexity of this marine colony. You’re looking at something that relatively few large marine animals outside of sea turtles and oceanic sunfish eat, and you’re also looking at an animal that produces stinging tentacles that a few other animals use to their advantage. The blue sea slug will feed on man ‘o war tentacles and incorporate the stinging cells into their own tissue. Other fish like the shepherd fish (which is partly immune to the venom and lives with the man-of-war) take advantage of the protection the stingers give when they swim among them.
Basically, they are cool organisms to see, and they serve important roles in the ecosystem. When you’re done admiring them, log the encounter in the memory banks as something to avoid touching next time.
Why I wrote this jellyfish article:
When I was a kid, my dad went on vacation to Florida, and came back with a horrific story of what he described as the most painful sting he’s ever encountered.
He was swimming in the shore-break when all of a sudden a breaking wave engulfed him and brought the tentacles of a jellyfish over his arm, waist and legs. Immediately the pain rushed through his body. As he fought to get free he tangled up more in the jellyfish.
Once on shore, he could look down and pick off the remaining tentacles on his leg. Already there were long red welts on his skin. He felt weak, almost fainted and had the urge to vomit. “Like my skin was on fire” he explained to me. Peeing on it apparently didn’t help (and as we’ll see, is a myth that actually makes it worse). In total, it took nearly 6 hours of intense pain for it to start easing up a bit. To this day he still has a small scar from that incident. The culprit, none other than the Portuguese man o’ war.
Prefer to Listen?
I recorded a narrated version of this article to make it more accessible.

